Monday, December 26, 2011
Nondisruptive upgrade of VMFS-3 to VMFS-5
Wednesday, December 14, 2011
Licensing: vSphere 5 Enterprise and 8 way VMs
With vSphere 5, 8 way VMs are now possible both in the Standard edition and Enterprise edition. For up to 32 way VMs, the Enterprise Plus license is required.
See link for more info, page 6.
Wednesday, December 7, 2011
VMXNET 3: Supported Guest Operating Systems
Saturday, November 26, 2011
P2V with VMware Converter Standalone 5 and sync feature
The video guides you through the migration wizard and discusses some relevant use cases for the sync feature.
Here's a link to Converter Standalone 5
Remember that as of v4.3 Windows Server 2000 is no longer supported as a source OS, so to convert win2k use Converter Standalone v4.01 in stead. In the release notes you can see supported guest operating systems.
Thursday, November 10, 2011
Downloading VMware tools seperately from VMware site
However, the different versions of VMware tools can also be downloaded directly from VMware's website on http://packages.vmware.com/tools. There are also tools version for Windows servers.
I found some more info on it on this site
Thursday, October 20, 2011
Got the new book by Scott Lowe - Mastering VMware vSphere 5
VMworld Europe 2012 announced - Barcelona
Tuesday, October 11, 2011
How to run XenServer 6.0 on vSphere 5 - with nested Windows Server 2008 R2 VM
To install XenServer 6.0 in a VM, first follow this guide to configure ESXi 5.0 (or watch this youtube video).
One important step is to execute the following command from the console:
echo 'vhv.allow = "TRUE"' >> /etc/vmware/config
Otherwise, configure like the guide. Once the custom VM has been created, to be able to choose ESXi 5 as operating system, go to Edit Settings -> Options -> Guest Operating System choose 'Other' and then choose VMware ESXi 5.x. This will ensure that you won't receive the "HVM is required for this operation" error when trying to boot the win2k8R2 vm (it is possible to change this after the install of XenServer as well).
Add the the XenServer to XenCenter
Create a new VM, choose win2k8 R2 64-bit, mount ISO, install.
Done.
Thursday, September 8, 2011
Upgrading vCenter v4.1 to v5.0
"The Fully Qualified Domain Name cannot be resolved. If you continue the installation, some features might not work correctly"
The reason for this error is that I had not created a reverse lookup on the DNS server. By following this guide, the issue was resolved and installation process could continue without further warnings.
Here are the screen dumps:
Configuring iSCSI for vSphere 5
Wednesday, August 17, 2011
vSphere 5 official release date
Update 2011.08.23: Well, vSphere 5 was not released yesterday as rumors would have it - so I guess we'll just have to wait and see. A guess, not completely unreasonable, would be sometime during this week or on the first day of VMworld in the US...
When: The official release date of vSphere 5 - for GA - has been set to Monday 2011.08.22.
Thursday, July 21, 2011
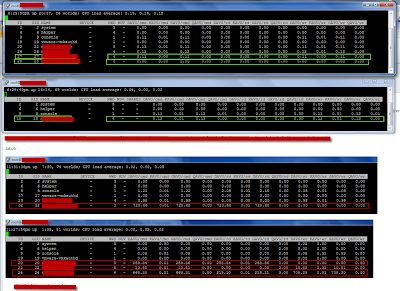
ESXTOP to the rescue - VM latency
Earlier on I have mostly used ESXTOP for basic troubleshooting reasons such as CPU ready and the like. Last weekend we had a major incident which was caused by a power outage which affected a whole server room. After the power was back on we had a number VMs that was showing very poor performance - as in it took about one hour to log in to Windows. It was quite random which VMs it was. The ESX hosts looked fine. After a bit of troubleshooting the only common denominator was that the slow VMs all resided on the same LUN. When I contacted the storage night duty the response was that there was no issue on the storage system.
I was quite sure that the issue was storage related but I needed some more data. The hosts were running v3.5 so troubleshooting towards storage is not easy.
I started ESXTOP to see if I could find some latency numbers. I found this excellent VMware KB article which pointed me in the right direction.
- For VM latency, start ESXTOP and press 'v' for VM storage related performance counters.
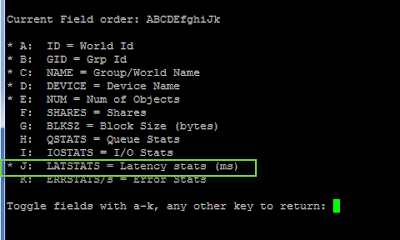
- The press 'f' to modify counters shown, then press 'h', 'i', and 'j' to toggle relevant counters (see screendump 2) - which in this case is latency stats (remember to stretch the window to see all counters)
- What I found was that all affected VMs had massive latency towards the storage system for DAVG/cmd (see screendump 1) of about 700 ms (rule of thumb is that max latency should be about 20 ms). Another important counter is KAVG/cmd which is time commands spend in the VMkernel, the ESX host, (see screendump 3). So there was no latency in the ESX host and long latency towards the storage system.
After pressing the storage guys for a while, they had HP come take a look at it, and it turned out that there was a defect fiber port in the storage system. After this was replaced everything worked fine and latency went back to nearly zero.

Sunday, July 17, 2011
Changing IP and VLAN on host - no VM downtime
- Enter maintenance mode
- Update the DNS entry on the DNS server
- Log on to the vCenter server and flush the DNS: ipconfig /flushdns
- Go to ILO, DRAC or something similar for the host (you will loose remote network connection when changing the IP) and change the IP (use this KB article for inspiration): [root@server root]# esxcfg-vswif -i a.b.c.d
-n w.x.y.z vswif0 , where a.b.c.d is the IP address and w.x.y.z i s the subnet mask. - Change the VLAN id (in this case VLAN 12): esxcfg-vswitch -v 12 -p 'Service Console' vSwitch0
- Change gateway: nano /etc/sysconfig/network
- Change DNS servers: nano /etc/resolv.conf
- Restart network: service network restart
- Ensure that gateway can be pinged
- Update the NTP server from the vSphere client if needed.
- Continue the process with next host in the cluster
Changing hostname from the service console
The easiest way to change the hostname is via the vSphere client (see this post for changing IP address and VLAN IP). If, however, this is not an option for some reason, the hostname can be changed from the service console the following way:
This KB article actually explains most of the proces which includes:
-----------------
1. Open the /etc/hosts file with a text editor and modify it so that it reflects the correct hostname.
2. To change the default gateway address and the hostname, edit the /etc/sysconfig/network file and change the GATEWAY and HOSTNAME parameters to the proper values.
3. For the changes to take place, reboot the host or restart the network service with the command:
[root@server root]# service network restart
Note: This command breaks any current network connections to the Service Console, but virtual machines continue to have network connection.
------------------------------
I have experienced that after a reboot, the changes are reset and the hostname is changed back to the original one. To avoid this, there is one more step to be performed (before reboot):
Change the /adv/Misc/HostName parameter in /etc/vmware/esx.conf file (see screendump)

Tuesday, June 28, 2011
Error during upgrade: The system call API checksum doesn’t match
On the ESX 4.0 host: Error during version check: The system call API checksum doesn’t match"
On the ESX 4.1 host: Vmkctl & VMkernel Mismatch,Signature mismatch between Vmkctl & Vmkernel
You can ignore the messages.
Workaround: Reboot the ESX 4.1 Update 1 host. "
Tuesday, June 21, 2011
Used network ports between ESX, vCenter, and the vSphere client
- A link to my previous post with a network diagram
- Link to VMware KB article about used ports for a vSphere environment and related components
- vMotion between networks requires TCP port 8000
- If searching and sorting VMs in the vSphere client is slow, then ensure that port 8443 TCP is opened between the vSphere client and the ESX hosts
- If hardware status tab is not available, then ensure that port 8443 TCP is opened between the vSphere client and the vCenter server
- In vCenter 5.x, if searching and sorting VMs in the vSphere client is slow then port 10443 TCP has to be opened between the vSphere client/client PC and the vCenter server (also, opening this port is required for viewing VM inventory across linked mode vCenter servers - for v5.1)
- If you can't get a remote console on the VMs (you get a black screen and a yellow bar in the top stating some sort of MKS error) ensure that port 903 (and 902) TCP is allowed from the vSphere client and to the ESX hosts
- If an ESX host keeps disconnecting in vCenter, ensure that port 902 UDP is allowed from the ESX host to the vCenter
Source
|
Destination
|
Direction
|
Protocol
|
Port
|
Purpose
|
vCenter
|
ESX
|
In/out
|
TCP
|
902
|
VMware console
|
vCenter
|
ESX
|
In/out
|
TCP
|
903
|
VMware console
|
vCenter
|
ESX
|
In/out
|
TCP
|
443
|
HTTPS
|
vCenter
|
ESX
|
In/out
|
TCP
|
22
|
SSH
|
vCenter
|
ESX
|
In/out
|
TCP
|
80
|
HTTP
|
vCenter
|
ESX
|
In/out
|
TCP
|
161
|
SNMP
|
vCenter
|
ESX
|
In/out
|
TCP
|
5989
|
CIM
|
ESX
|
vCenter
|
out
|
UDP
|
902
|
Heartbeart
|
Tuesday, May 10, 2011
vSphere Network Ports Diagram

Monday, April 18, 2011
Installing View 4.6 in home lab



Sunday, April 17, 2011
My ESXi home lab - the Blue Bad Boy














































